- *Corresponding Author:
- A. Kumar
University Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Panjab University, Chandigarh-160 014, India
E-mail: bashwani@pu.ac.in
| Date of Submission | 29 June 2016 |
| Date of Revision | 28 February 2017 |
| Date of Acceptance | 14 August 2017 |
| Indian J Pharm Sci 2017;79(5):834-838 |
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms
Abstract
Ferula sumbul (Umbelliferae) roots have a characteristic musk odour and it has been traditionally used for relieving anxiety, as a sedative in hysteria and other nervous disorders. Present investigation aims to develop and validate a simple, robust, accurate and fast analytical ultra-performance liquid chromatography technique for the estimation of valerenic acid in F. sumbul roots. F. sumbul root extract was prepared by refluxing the powdered roots with methanol for 30 minutes. A simple method for the estimation of valerenic acid has been developed and validated using ultra-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detector. The estimation was achieved using BEH Shield RP, C-18 column (2.1×50 mm, 1.7 μm) with isocratic elution of methanol and 0.5% phosphoric acid (75:25) at a flow rate of 0.25 ml/min and detection at 218 nm. The method has been developed for the first time and is accurate with good linearity (r2>0.998). F. sumbul roots were found to contain 12.62±0.074 µg/g valerenic acid. The developed method can be selectively used for the estimation of valerenic acid in the roots of F. sumbul. All the validation parameters were found to be within the permissible limits prescribed by ICH guidelines.
Keywords
Ultra-performance liquid chromatography, valerenic acid, F. sumbul, validation
The genus Ferula (Umbelliferae) comprises 130 species distributed from the Mediterranean region to Central Asia. The genus is well documented as a good source of biologically active compounds such as coumarins, terpene alcohols, and sesquiterpene derivatives [1]. F. sumbul Hook. (Syn. F. moschata Reinsch.) commonly known as sumbul (Hindi) or musk root (English) consists of cylindrical or tapered pieces of dried roots and rhizomes with bitter taste and slight musky odour [2]. It has been traditionally used for relieving anxiety, as a sedative in hysteria and other nervous disorders, and as a mild gastrointestinal stimulant. The coumarins and bicoumarins isolated from the ethanol extract of F. sumbul roots exhibit antiHIV activity and inhibit cytokine release [3].
The present study involves the estimation of valerenic acid (VA, Figure 1) content in F. sumbul roots, using ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). VA is one of the important constituents of the drug Valeriana officinalis [4,5] and is mainly responsible for its anxiolytic activity. Its root extract has been used for the treatment of anxiety, epilepsy and sleep disorders for centuries. UPLC, a derivative of wellknown analytical technique, works on the same basic principle of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), but decreased column particle size allows increased sensitivity, better resolution and shorter run time [6,7]. Already established HPLC method for VA estimation involves a complex solvent system for its quantification [8,9]. The UPLC method described herein has shorter run time, consumes less HPLC solvent and reference standard, and gives better separation and enhanced resolution.
Roots of F. sumbul were procured from Rym Exports, Mumbai, India. They were authenticated from NISCAIR, New Delhi, with voucher specimen number NISCAIR/RHMD/Consult/2014/2483-62-2 dated 18/07/2014. Reference standard VA was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, HPLC grade methanol was obtained from Merck Specialties Pvt. Ltd. (Mumbai, India) and HPLC grade water was obtained from the Millipore system (Billerica, MA, USA).
Accurately weighed 1 mg of VA was dissolved in methanol and volume was made up to 10 ml in a volumetric flask, to get a concentration of 100 μg/ml. This was used as stock solution, to make the further dilutions. The coarsely powdered roots of F. sumbul (2 g) were refluxed for 30 min with HPLC-grade methanol (20 ml). The extract obtained was filtered through Whatmann filter paper (no. 10). The residue was washed with methanol (5 ml), transferred to 25 ml volumetric flask and the volume was adjusted to get a concentration of 80 mg/ml. It was filtered through 0.22 μm syringe filter. The sample solution (0.50 μl) was injected into the UPLC system. The whole process was carried out in triplicate.
Analysis was performed on a Waters Acquity UPLC H-Class system, equipped with a binary pump, autosampler, photodiode array detector (PDA) and Empower 2™ software (Waters, Milford, MA, USA). The analytical method was developed using a BEH Acquity RP, C-18 column (2.1×50 mm, 1.7 μm, Waters, Milford, MA, USA). The mobile phase consisted of methanol (solvent A) and 0.5% phosphoric acid (solvent B), in the ratio of 75:25. The flow rate was set to 0.25 ml/min, injection volume was 0.50 μl, column temperature was maintained at 25° using a column oven, and detection was carried out using PDA detector at 218 nm.
The developed UPLC method was validated in accordance with ICH (Q2 (R1)) guidelines in terms of linearity, sensitivity, precision, accuracy, and robustness of the study [10]. Linearity was determined using concentration levels plotted over the range of 0.5-2.0 μg/ml. The calibration curve was developed by plotting peak area versus concentration. The regression coefficient, slope and intercept were calculated from the calibration curve. Sensitivity of the method was determined with respect to limit of detection (LOD, S/N=3) and limit of quantification (LOQ, S/N=10). Serial dilutions of the standard solution were injected and, thus, LOD and LOQ values were calculated by the UPLC system suitability software. Repeatability of the method was analysed by injecting single concentration of VA six times (n=6) within one day. The precision data were expressed as percentage relative standard deviation (%RSD). For determination of accuracy of the method, a recovery study was carried out by adding a known amount of individual standard at low (80%), medium (100%) and high (120%) concentration into coarsely powdered drug and the sample was prepared as described earlier. The three concentrations, thus prepared, were analysed in triplicate and the results were expressed as the percentage recovery of the added standard. Robustness of the method was determined by making deliberate changes to the chromatographic conditions, such as change in flow rate (0.25±0.02 ml/min), mobile phase composition (75:25±5) and injection volume (0.5±0.1 μl). Each parameter was analysed in triplicate and the variations in the retention time were expressed as %RSD with respect to normal retention time.
Optimal chromatographic conditions were obtained on the Acquity BEH Acquity, RP C-18 column and isocratic elution using different proportions of methanol: 0.5% aqueous phosphoric acid (75:25) as mobile phase for the method development for VA by UPLC. The optimised chromatographic conditions led to well separated peak of VA in methanol extract of F. sumbul roots, with a stable baseline.
The validation of the developed method was done by preparing the standard curve of VA. For VA standard, the correlation coefficient (r2) was found to be ≥0.998, which indicates a high degree of correlation between selected concentrations and respective peak areas, and also indicated good linearity of the method developed. The slope, intercept and correlation coefficient for the standard were determined by regression analysis. The LOD for VA was observed to be 30 ng/ml and LOQ was 100 ng/ml implying adequate sensitivity of the method (Table 1). The %RSD values for repeatability studies were found to be 0.506%, which complied with permissible limits (≤5) as per the ICH guidelines (Table 1). Percent recovery for VA standard was found to be in the range of 99.44-102.02 with %RSD≤1.311 (Table 2), which showed good recovery of the standard. The %RSD values for all the deliberately made changes in the UPLC conditions were found to be in the acceptable range: for flow rate, 0.038-0.311; for mobile phase composition, 0.035-0.605; for injection volume, 0.161-0.395. For the different parameters taken into consideration, the %RSD values were less than 5%, which clearly indicates the robustness of the analytical method (Table 3).
| Parameter | Observations |
|---|---|
| LOD | 30 ng/ml |
| LOQ | 100 ng/ml Range: 0.5-2.0 µg/ml |
| Linearity | Regression equation: y=16188x–79.30 Correlation coefficient: r2=0.998 |
| Repeatability (n=6) %RSD | 0.507 |
LOD: limit of detection; LOQ: limit of quantification; %RSD: percentage relative standard deviation
Table 1: LOD, LOQ, linearity and precision of UPLC method for quantifying VA
| Original amount in sample (µg/ml) (n=9) |
Spiked amount (µg/ml) | Found amount (µg, n=3) | Mean recovery (n=3) |
Mean recovery (n=9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.010±0.006 (0.586) | 0.8 | 1.804±0.016 (0.917) | 99.438±2.068 (2.079) | 100.896±1.322 (1.311) |
| 1 | 2.027±0.002 (0.094) | 101.230±0.190 (0.187) | ||
| 1.21 | 2.244±0.026 (1.81) | 101.019±2.191 (2.148) |
All values are given as mean±SD (%RSD)
Table 2: Results of recovery studies
| Parameter | Variable parameter | Sample | Mean retention time | %RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow rate (0.25±0.02) |
0.23 | Test | 3.721 | 0.038 |
| Standard | 3.722 | 0.113 | ||
| 0.27 | Test | 3.184 | 0.311 | |
| Standard | 3.164 | 0.223 | ||
| Mobile phase composition (75:25±5) |
70:30 | Test | 5.958 | 0.605 |
| Standard | 5.966 | 0.130 | ||
| 80:20 | Test | 3.317 | 0.256 | |
| Standard | 2.031 | 0.035 | ||
| Injection volume (0.50±0.1) | 0.40 | Test | 3.582 | 0.395 |
| Standard | 3.524 | 0.241 | ||
| 0.60 | Test | 3.543 | 0.359 | |
| Standard | 3.501 | 0.162 |
For the different parameters taken into consideration, the %RSD values were less than 5%, which clearly indicates the robustness of the analytical method
Table 3: Robustness of the method
The UPLC/PDA method developed was employed for quantification of VA in the sample of F. sumbul roots. Figure 2 depicts the chromatogram of the drug, VA and blank. Mean VA content in the roots was estimated to be 12.62±0.074 μg/g with %RSD 0.548.
Aim of the present investigation, was to develop a fast, accurate and robust analytical method for VA estimation. VA is considered to be the main constituent responsible for the central nervous system activities and has been officially reported as a marker compound of V. officinalis [11,12]. The main purpose of the study was to describe a UPLC method, which could be used for the quantification and standardization of F. sumbul roots. The proposed method has a short run time of 7 min, with retention time of around 3.2 min. With such a short time of analysis and good resolution, the method offers substantial advantages over earlier reported HPLC methods [8] and hence can be extended for analytical purposes.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge University Grants Commission (UGC) for the financial support of this study.
Financial assistance
Nill.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gonzalez A, Barrera J. Chemistry and sources of mono- and bicyclic sesquiterpenes from Ferula species.In: Herz W, Kirby GW, Moore RE, Steglich W, Tamm C, editors. Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products. Vol. 64. New York: SpringerLink; 1995.
- The Wealth of India. A Dictionary of Raw Materials and Industrial Products, Raw Materials. Vol. 4, New Delhi: Publications and Information Directorate, CSIR; 1956. p. 21-22.
- Zhou P, Takaishi Y, Duan HQ, Chen B, Honda G, Itoh M, et al. Coumarins and bicoumarin from Ferula sumbul: antiHIV activity and inhibition of cytokine release. Phytochemistry 2000;53:689-97.
- Khom S, Strommer B, Ramharter J, Schwarz T, Schwarzer C,Erker T, et al. Valerenic acid derivatives as novel subunit-selective GABA(A) receptor ligands - in vitro and in vivo characterization. Br J Pharmacol 2010;161:65-78.
- Nam SM,Choi JH, Yoo DY, Kim W, Jung HY, Kim JW, et al. Valeriana officinalis extract and its main component, valerenic acid, ameliorate D-galactose-induced reductions in memory, cell proliferation, and neuroblast differentiation by reducing corticosterone levels and lipid peroxidation. Exp Gerontol 2013;48:1369-77.
- Bairwa K, Srivastava A, Jachak SM. Quantitative analysis of boeravinones in the roots of Boerhaavia diffusa by UPLC/PDA. Phytochem Anal 2014;25:415-20.
- Kumar A, Saini G, Nair A, Sharma R. UPLC: A preeminent technique in pharmaceutical analysis. Acta Pol Pharm 2012;69:371-80.
- Bos R, Woerdenbag H, Hendriks H. The Essential Oil and Valepotriates from Roots of Valeriana javanica Blume Grown in Indonesia. Flavour Fragr J 1996;11:321-26.
- Gao X, Björk L. Valerenic acid derivatives and valepotriates among individuals, varieties and species of Valeriana. Fitoterapia 2000;71:19-24.
- https://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q2_R1/Step4/Q2_R1__Guideline.pdf.
- The European Pharmacopoeia. Vol. 2. Strasbourg, France: Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare of Council of Europe, EDQM; 2011. p. 1269-63.
- Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission. New Delhi: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; 2014. p. 3276-78.
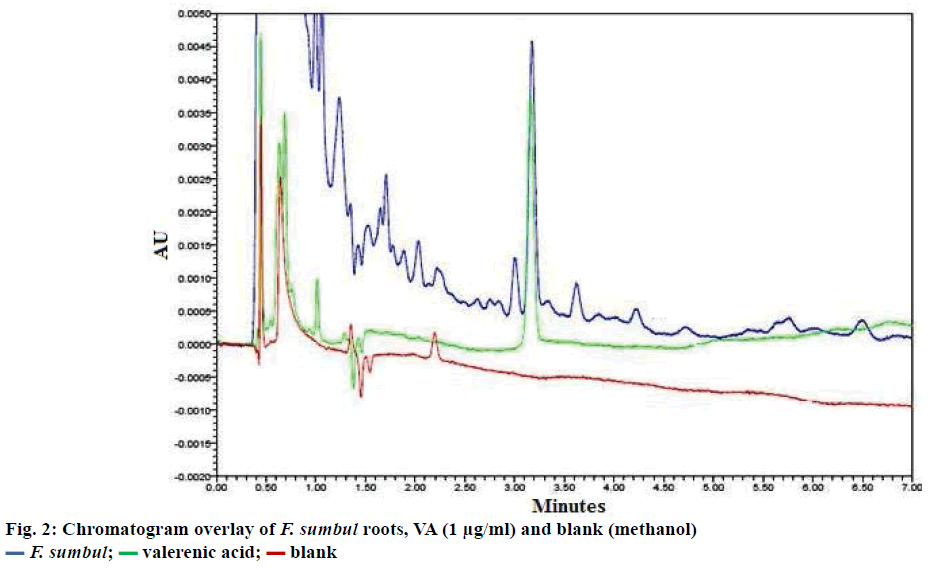
 F. sumbul;
F. sumbul;  valerenic acid;
valerenic acid;  blank
blank