- *Corresponding Author:
- K. Anandakumar
Adhiparasakthi College of Pharmacy, Melmaruvathur - 603 319, India
E-mail: anandkarunakaran@yahoo.com
| Date of Submission | 7 April 2006 |
| Date of Revision | 20 March 2007 |
| Date of Acceptance | 15 August 2007 |
| Indian J Pharm Sci, 2007, 69 (4): 597-599 |
Abstract
A reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography method was developed for the simultaneous estimation of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate in formulation. The separation was achieved by octadecyl column (C 18 ) and acetonitrile:methanol:20 mM phosphate buffer at pH 3 (50:7:43 v/v) as eluent, at a flow rate of 1 ml/min. Detection was carried out at 240 nm. Quantitation was done by external standard calibration method. The retention time of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate was found to be 2.40 and 9.27 min, respectively. The method has been validated for linearity, accuracy and precision. Linearity for aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate were in the range of 10-50 µg/ml for both the drugs. The mean recoveries obtained for aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate were 100.86% and 100.20%, respectively. The developed method was found to be accurate, precise, selective and rapid for the simultaneous estimation of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate in capsules.
Keywords
RP-HPLC, aspirin, clopidogrel bisulphate, simultaneous estimation, method development and method validation
Aspirin, 2-acetoxy benzoic acid is cyclo oxygenase inhibitor. It is used as an analgesic, antipyretic, antiin flammatory and anti thrombic agent [1]. Clopidogrel bisulphate is methyl (s)-2-chlorophenyl (4,5,6,7- tetrahydrothieno- [3,2-C]pyridin-5-yl) acetate bisulphate, an ADP antagonist. It is used as an anti thrombic agent [2,3]. A capsule formulation containing 75 mg of aspirin and 75 mg of clopidogrel bisulphate is available (Combiplet, Sidmak Laboratories). Aspirin is official in IP [4], BP [5] and USP [6] but clopidogrel bisulphate is not official in any pharmacopoeia. A survey of literature revealed that spectrometric method was reported for the determination of aspirin in biological fluids [7]. RP-HPLC methods were reported for the simultaneous estimation of aspirin, paracetamol, caffeine [8] and aspirin with atorvastatin [9]. Spectrofluorimetric method also developed for the estimation of aspirin and dipyridamole [10]. Colorimetry [11], HPLC [12] and gas chromatographic [13] methods were described in the literature for the estimation of clopidogrel bisulphate. However no HPLC method for the simultaneous estimation of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate in combined dosage forms has so far been reported. The present work describes the development of a simple, precise and accurate reverse phase HPLC method for the simultaneous estimation of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate in capsules.
The pure drug samples of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate were obtained as gift samples from Tristar Pharmaceuticals, Pondicherry. Qualigens Fine Chemicals, Mumbai, supplied HPLC grade acetonitrile, methanol and water, sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate AR grade and phosphoric acid AR grade. An isocratic high pressure liquid chromatograph (Schimadzu HPLC class VP series) with LC-10 ATVP pump, variable wavelength programmable UV/Vis detector SPD –10AVP system and operating software winchrom was used. The chromatography column used was a reverse phase phenomenax C18 column (250 mm×4.6mm i.d, particle size 5µ).A mixture of acetonitrile, methanol and 20 mM phosphate buffer (adjusted to pH 3 using ortho phosphoric acid) in the ratio of 50:7:43 v/v was used as mobile phase and was filtered before use through 0.45 µ membrane filter. The flow rate of mobile phase was maintained at 1 ml/min. Detection was carried out at 240 nm at the temperature of 20°.
Standard stock solutions of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate (100 µg/ml) were prepared in mobile phase. The standard solutions were further diluted in mobile phase containing a mixture of 30 µg/ml of aspirin and 30 µg/ml of clopidogrel bisulphate. Twenty capsules of Combiplet (Sydmak Laboratories) each containing 75 mg of aspirin and 75 mg of clopidogrel bisulphate were weighed, empty the capsules and finely powdered. A quantity of powder equivalent to 50 mg of aspirin was weighed and transferred into a 50 ml volumetric flask. The drugs were extracted with the mobile phase. The extracts were made up to the volume (50 ml) with mobile phase and further dilutions were made to get a concentration of 30 µg/ml of both aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate. The contents were mixed thoroughly and filtered through 0.45 µ membrane filter. An aliquot of 20 µl of both standard and test solutions were injected separately and chromatograms were recorded up to 10 min.
The present investigation was aimed at developing a simple, precise and accurate HPLC method to estimate aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate in capsules using widely used RP-HPLC C18 column (phenomenax). The mobile phase was optimized with acetonitrile, methanol and 20mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 3), in the proportion 50:7:43 v/v. With the above mentioned composition of mobile phase, sharp peaks with good resolution between aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate was achieved with reasonable short run time of 10 min. The criteria employed for assessing the suitability of above said solvent system were cost, time required for analysis, solvent noise, preparatory steps involved in the use of same solvent system for the extraction of the drugs from the formulation excipient matrix for the estimation of the drug content. UV detection was carried out at 240 nm as aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate showed good absorbance at this wavelength.
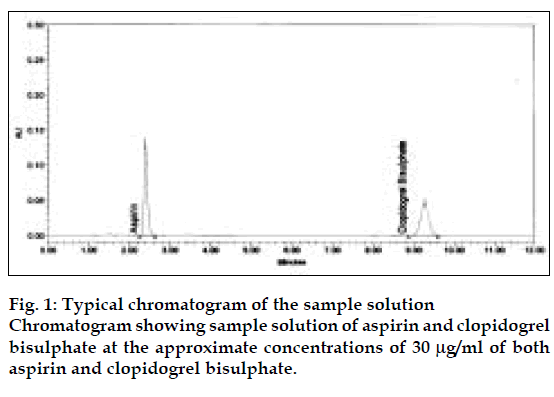
The retention time of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate was found to be 2.40 and 9.27 min, respectively. A typical chromatogram of test solution is shown in fig. 1. The capacity factors (k′ ) of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate were found to be 2.21 and 5.97, respectively. The peak shapes of both the drugs were symmetrical and the asymmetry factor was less than 2. The response factor of the standard and the test solutions was calculated. The proposed method was validated as per the standard analytical procedures [14]. Each of the sample was injected six times and the retention time was observed in all the cases. Precision of the proposed method was found to be 0.272% for aspirin and 0.535% for clopidogrel bisulphate. The low %RSD values indicated that the proposed method had good precision. Linearity experiments were performed thrice for both the components and the response was found to be in the range of 10-50 µg/ml for both drugs. Linearity of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate was plotted by a graph of peak area versus concentration. The correlation coefficient ‘r’ values (n=3) for both aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate were 0.9997 and 0.9996, respectively. Accuracy of the method was calculated by recovery studies (n=3) at five levels. Standard drug solutions containing drugs in the range 20%, 30%, 40%, 50% and 60% of nominal concentration (30 µg/ml for both aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate) was added to previously analysed test solution. Amount of drug recovered at each level was calculated. Table 1 shows the data from the recovery study for aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate were 100.8% and 100.20%, respectively. The sample recovery in the formulation was in good agreement with the label claim. High percentage recovery showed that the method was free form interference of the excipients used in formulations. System suitability parameters of aspirin and clopidogrel bisulphate are given in Table 2. Assay of the combination in capsule dosage form was found to be 100.42% of aspirin and 101.22% of clopidogrel bisulphate. The method was simple and had short run time of 10 min, which makes the method rapid. The results of the study indicate that the proposed HPLC method is simple, precise, accurate and less time consuming.
| Drug | Amount added(µg/ml) (n=3) | Amount recovered(µg/ml) (n=3) | Recovery(%) | Averagerecovery±SD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspirin | 3.00 | 3.03 | 101.00 | 100.86±0.424 |
| 4.50 | 4.54 | 100.89 | ||
| 6.00 | 6.01 | 100.17 | ||
| 7.50 | 7.60 | 101.33 | ||
| 9.00 | 9.08 | 100.89 | ||
| Clopidogrel | 3.00 | 3.01 | 100.33 | 100.20±0.387 |
| bisulphate | 4.50 | 4.53 | 100.67 | |
| 6.00 | 6.01 | 100.16 | ||
| 7.50 | 7.47 | 099.60 | ||
| 9.00 | 9.02 | 100.2 |
Table 1: Recovery Studies
| Parameter | Aspirin | Clopidogrelbisulphate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tailing factor | 1.23 | 1.02 | |
| Theoretical plates | 3999 | 10151 | |
| Capacity factor | 2.21 | 5.97 | |
| Resolution factor | 16.04 | ||
| Calibration range | 10-50 µg/ml | 10-50 µg/ml | |
Table 2: System suitability parameters
References
- Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology. 5thed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd; 2004,560.
- Satoskar RS, Bhandarkar SD, Ainapure SS, editors. Pharmacology and Pharmaco- therapeutics. 15thed. Mumbai: Popular Prakashan; 1997, 462.
- Budavari, S, eds., In; The Merck Index. 12thed. New Jersey: Merck and Co., Inc; 1996 406.
- The Indian Pharmacopoeia, 4thed. Vol. I, New Delhi: The controller of publications; 1996, 69.
- British Pharmacopoeia, International edition, Vol. II. London: HMSO; 1993, 780.
- United States Pharmacopoeia, National Formulary USP23, Asian Edition, Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopoeial Convention, Inc; 1995, 133, 135, 1776, 1982.
- Ahmed M, Biswas HU, Sadik G. Development of a spectrometric method for the determination of aspirin in blood samples. J Med Sci. 2001;1 suppl.2:61-62.
- Satinsky D, Neto I, Solich P, Sklenakova H, Conceicao M, Montenegro BS, Araujo AN. Sequential injection chromatographic determination of paracetamol, caffeine and acetyl salicylic acid in pharmaceutical tablets. J Sep Sci. 2004;27 suppl.7:529-536.
- Manoj K, Shanmugapandiyan P, Anbazhagan S. RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of atorvastatin and aspirin from capsule formulations. Indian Drugs 2004;41 suppl.5:284-289.
- Umapathi P, Parimoo P, Thomas SK, Agarwal V. Spectrofluorimetric estimation of aspirin and dipyridamole in pure admixtures and in dosage forms. J Pharm Biomed Anal 1997;15 suppl. 11:1703-1708.
- Mishra P. Dolly A. Development of UV spectrophotometric method for the determination of clopidogrel in tablet dosage form. Indian J Pharm Sci 2005;67:491-493.
- Mitakos A. Panderi I. A Validated LC method for the determination of clopidogrel in pharmaceutical preparations. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2002;28 suppl. 3-4, 431-438.
- Kample NS. Venkatachalam A. Estimation of clopidogrel from tablet dosage form by gas chromatographic method.Indian J Pharm Sci 2005;67:128-129.
- International Conference on Harmonisation, Guidance for Industry In; Q2B Validation on Analytical Procedures: Methodology. Switcherland: IFPMA 1996;1-8.