- Corresponding Author:
- k. Ambre
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry
Bombay College of Pharmacy, Kalina
Santacruz (E), Mumbai-400 098, India
E-mail: premlata.ambre@gmail.com
| Date of Submission | 10 July 2013 |
| Date of Revision | 17 January 2014 |
| Date of Acceptance | 24 January 2014 |
| Indian J Pharm Sci 2014;76(2):116-124 |
Abstract
Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase is an important target for antimalarial chemotherapy. The emergence of resistance has significantly reduced the efficacy of the classic antifolate drugs cycloguanil and pyrimethamine. In this paper we report new dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors identified using molecular modelling principles with the goal of designing new antifolate agents active against both wild and tetramutant dihydrofolate reductase strains three series of trimethoprim analogues were designed, synthesised and tested for biological activity. Pyrimethamine and cycloguanil have been reported to loose efficacy because of steric repulsion in the active site pocket produced due to mutation in Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase. The synthesised molecules have sufficient flexibility to withstand this steric repulsion to counteract the resistance. The molecules have been synthesised by conventional techniques and fully characterised by spectroscopic methods. The potency of these molecules was evaluated by in vitro enzyme specific assays. Some of the molecules were active in micromolar concentrations and can easily be optimised to improve binding and activity.
Keywords
pf DHFR, malaria, antifolate, 3D−QSAR, docking
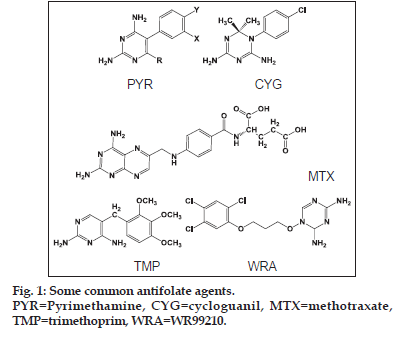
Malaria is one of the oldest diseases known and is still a major cause of mortality throughout the world especially in equatorial regions. Antifolate agents (fig. 1) like pyrimethamine (PYR), cycloguanil (CYG) and trimethoprim (TMP) along with many other related compounds are the first line of treatment of malaria[1]. In fact, many chemically diverse compounds have been reported to inhibit the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase of Plasmodium falcifarum (pfDHFR) like diaminopyridines (e.g. PYR and TMP), diaminotriazines (e.g. CYG), diaminoquinazolines and diaminopteridines (e.g. methotrexate)[2]. Recently, few more heterocycles containing the diamino functionality have been introduced, which include aminopyrido (4,3−b) indole and triazinobenzimidazoles[3].
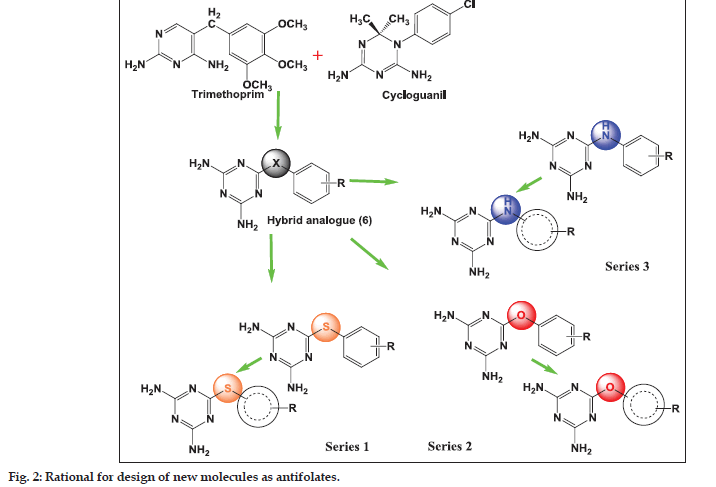
The goal of the current study was to identify molecules active against both the wild and mutant strains. Of the several core structures mentioned earlier, new pfDHFR inhibitors were designed around the triazine core. The rationale of developing analogues around the diminotriazino nucleus was based on the recently disclosed antifolates, for example WR99210 with a similar core[4] and JPC2067[5]. Our molecules are a hybrid of both CYG and TMP as shown in (fig. 2). The core nucleus is diaminotriazine (like CYG) with an aryl group at the 6−position; the only difference from TMP is the linker joining the two rings and the absence of the trimethoxy group. Thus these molecules could be classified as diaromatic amines, ethers and thioethers of triazine.
Materials and Methods
The computational studies were carried on a personal computer (PC) with an AMD 3.0 GHz processor and 3.0 GB RAM with CentOS as the operating system. The structures of the molecules were built and their geometries optimised with the suite of programs in Sybyl 7.1 (Tripos Inc. USA)[6]. The 3D−QSAR studies were carried out with CoMFA[7,8] module in Sybyl 7.1. Molecular docking was carried out with GOLD v3.0.1 (CCDC UK[9];).
Molecular Docking; Preparation of ligands
The 3D structures of the molecules belonging series 1 (triazinoaryl ethers), 2 (triazinoaryl thioethers) and 3 (arylanilinotriazine), (Table 1) along with TMP derivatives[10] (Data not shown) were built with Sketch wizard of Sybyl 7.1 (Tripos Inc. USA). The geometries of the molecules were optimised by energy minimisation using the Powel method with the Tripos force field and Gasteiger Hückel charges for all atoms, until a gradient 0.01 kcal/mol/Å was reached. The dielectric constant was set to 1.0.
Preparation of protein
The X−ray crystal structures of both wild type and tetramutant forms of pfDHFR with PDB code 1J3I (wild type) and 1J3K (tetramutant)[11] were used for the design of new DHFR inhibitors. The enzyme exists as a dimer in the crystal. The docking studies were carried out with the monomer, as the active site resides deep within the enzyme. All water molecules were deleted from the crystal structure since no water molecule has been reported to be conserved and important. The intrinsic ligands were deleted while the cofactor, which is the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) was retained. This was followed by ‘cleaning’ the structure and addition of hydrogens to all heavy atoms and the assignment of charges to atoms with the Biopolymer module in Sybyl 7.1. For compatibility with the GOLD program, Sybyl atom and bond types were assigned to the protein atoms. The side chains of aspartate, glutamate, lysine and arginine residues were kept in their ionised state corresponding to pH 7.4, while histidine was unprotonated (corresponding to the δ tautomer) at this pH.
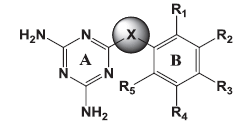 |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecules | X | Ring B | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | |
| S1-1 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -H | -H | -H | |
| S1-2 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -NO2 | -H | -H | |
| S1-3 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -Cl | -H | -H | |
| S1-4 | -O- | Phenyl | -Cl | -H | -H | -H | -H | |
| S1-6 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -OCH3 | -H | -H | |
| S1-7 | -O- | α-Naphthyl | - | - | - | - | - | |
| S1-8 | -O- | β-Naphthyl | - | - | - | - | - | |
| S1-9 | -O- | Phenyl | -CH3 | -H | -H | -CH3 | -H | |
| S1-10 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -CH3 | -H | -CH3 | -H | |
| S1-11 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -CH3 | -H | -H | -H | |
| S1-15 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -Phenyl | -H | -H | |
| S1-16 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -tBu | -H | -H | |
| S1-17 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -CH3 | -Cl | -H | -H | |
| S1-32 | -O- | Phenyl | -OCH3 | -H | -H | -H | -OCH3 | |
| S2-3 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -F | -H | -H | |
| S2-4 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -O (Benzyl) | -H | -H | |
| S2-5 | -S- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -H | -H | -H | |
| S2-7 | -S- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -Cl | -H | -H | |
| S2-11 | -S- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -CH3 | -H | -H | |
| S2-42 | -S- | Phenyl | -NH2 | -H | -H | -H | -H | |
| S3-1 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -H | -H | -H | |
| S3-2 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -NO2 | -H | -H | |
| S3-3 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -Cl | -H | -H | |
| S3-4 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -OCH3 | -H | -H | |
| S3-9 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -CH3 | -H | -H | |
| S3-10 | -NH- | Phenyl | -CH |
3 |
-H | -H | -H | -H |
| S3-21 | -NH- | 2-pyridyl | - | -H | -H | -CH | -H | |
|
3 |
||||||||
| S3-29 | -NH- | 3-pyridyl | -H | - | -H | -H | -H | |
| S3-40 | -NH- | Phenyl | -OCH3 | -H | -H | -H | -H | |
| S3-41 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -OCH3 | -H | -H | -H | |
| S3-42 | -NH- | Phenyl | -Cl | -H | -Cl | -H | -H | |
| S3-45 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -Cl | -H | -H | -H | |
| S3-46 | -NH- | Phenyl | -Cl | -Cl | -H | -H | -H | |
| S3-50 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -Cl | -F | -H | -H | |
| S3-53 | -NH- | Phenyl | -CH3 | -H | -CH3 | -H | -H | |
| S3-54 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -COCH3 | -H | -H | -H | |
| S3-55 | -NH- | N-CH3, | -H | -H | -H | -H | -H | |
| N-Phenyl | ||||||||
| S3-56 | -NH- | N, | -H | -H | -H | -H | -H | |
| N-diPhenyl | ||||||||
| S3-57 | -NH- | Phenyl | -C2H5 | -H | H | -H | -H | |
| S3-58 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -iPr | -H | -H | |
Table 1: chemical structure of synthesised Compounds.
Docking protocol
The docking protocol was set, only after it was confirmed that the protocol could reproduce the pose of the bound ligand as seen in the crystal. The configuration of WR99210 in the crystal structures of pfDHFR (PDB codes 1J3I and 1J3K) was used for an initial alignment of other ligands in the active site (defined by residues enclosed within a 10.0 Å radius from the centroid of WR99210) of the enzyme. The active site is demarcated by residues Ile14, Asp54, Met55, Asn108, Leu164 and Thr185. The side−chain of Met55 was set ‘flexible’ in the docking protocol to enable proper positioning of the potent PYR and CYG derivatives. The parameters in GOLD modified/optimised for the docking studies were (a) the dihedral angles of the ligand; (b) the ligand ring geometries (flipping ring corners); (c) the dihedral angles of protein OH and groups; and (d) mappings of the H−bond fitting points. At the start of a docking run, all these variables were randomised. The docking was carried for 20 GA runs, which was found optimum to reproduce the crystal structure. Most of the other GA parameters like population size and the genetic operators were left at their default values. For ranking the poses of the molecules the default scoring function “GoldScore” was utilised. The best docking solutions were saved for each molecule and were used for further studies.
3D−QSAR studies
3D−QSAR studies were performed on a series of TMP derivatives reported as potent inhibitors of both the wild and tetramutant species. The molecules were built, optimised and docked into the two proteins using the same protocol mentioned earlier. By this procedure ligand–protein complexes of the TMP derivatives were generated. The best−scored complexes were aligned using sequence and the structure of the protein to build the “receptor−based alignment” necessary for the CoMFA/CoMSIA studies. Later the protein portions were deleted before the start of the CoMFA/CoMSIA studies (fig.3). The aligned molecules were divided in test and training sets based on their physicochemical properties with the CombiChem I utility in the Cerius2 molecular modelling suite[12]. The goal of the 3D−QSAR studies was twofold, first to delineate the differences in structure that are necessary for inhibition of wild and mutant species and second to build a model that could be used for prediction of the activity of new compounds.
Synthesis
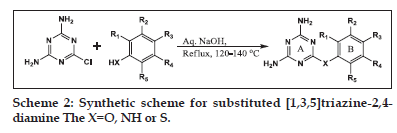
The molecules (Table 1) were synthesised by established procedures[13,14] as shown in Schemes 1 and 2. The procedures were modified to improve the yield and purity of the products. All solvents and reagents used for synthesis were of laboratory grade. The reactions were monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC) using Merck precoated silica plates (GF 254) for completion of the reaction and for establishing the purity. The melting points were recorded in open capillaries on an electrically heated melting point apparatus and are uncorrected. IR spectra were recorded (KBr disc method) on a Jasco FT−IR 5300 spectrophotometer. 1H NMR spectra for some representative structures were recorded on a 300 MHz Bruker AN 300 instrument. Chemical shifts are reported in ppm down field from tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the internal standard. Mass spectra were also carried out for some representative compounds. Spectroscopic details for representative molecules are provided in the Table 2.
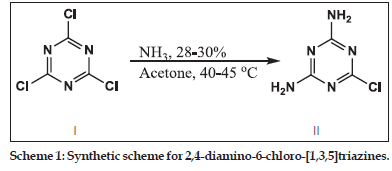
Synthesis of 2,4−diamio−6−chloro−[1,3,5]triazine (II)
In a 250 ml dry round bottom flask, cyanuric chloride (I) 5.0 g, (0.02711 mole) was taken and dissolved in 80 ml of hot acetone. To this solution, 7.36 ml (0.1085 mole) of ammonia and 28 ml of water was added and the reaction mixture was refluxed at 40–45° for 5 h. On completion of the reaction, the product was isolated by filtration and washed well with distilled water to remove chloride impurities. The product was dried in an oven at 100°.
General procedure for synthesis of diaminotriazine derivatives
In a 250 ml round bottom flask, 2,4−diamino- 6−chloro−1,3,5−triazine (II) 1.45 g (0.01 mole) was mixed with equimolar quantities of substituted phenols or thiols and 0.4 g (0.01 mole) sodium hydroxide in 50 ml of water. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature (RT) for 15 min and then refluxed for 6–12 h with constant stirring. The crude products were isolated by filtration and washed with 100 ml distilled water, 25 ml methanol, then dried in an oven at 100° and recrystallised from n−butanol.
General procedure for synthesis of arylanilinotriazine derivatives
In a 250 ml round bottom flask, 1.45 g (0.01 moles) of (II) and equimolar amounts of substituted anilines was suspended in appropriate solvent, that is 40 ml dimethyl formamide or 60–120 ml water. The reaction mixture was refluxed at 130–140° with constant stirring for 6–11 h. On completion of the reaction, the mixture was basified using 0.4 g (0.01 moles) sodium hydroxide in 50 ml water. The precipitated product was filtered and washed free of chloride ion with approximately 100–150 ml distilled water. The product was recrystallised from ethanol and dried in oven at 100°.
Biological evaluation for antimalarial activity
Fifteen molecules (Table 3) from the synthesised molecules were tested for in vitro pfDHFR specific inhibition of both wild and quadruple mutant strains. The inhibitory activity was determined spectrophotometrically at 25° using a Hewlett Packard UV/Vis spectrophotometer (HP 8453). The catalytic reaction (1 ml) contained DHFR buffer (50 mM TES, pH 7.0, 75 mM b−mercaptoethanol, 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin), 100 μM each of the substrate dihydrofolate, the cofactor, reduced NADPH and an appropriate amount (0.001–0.005 units in phosphate buffer containing 50 mM KCl) of purified enzyme to initiate the reaction. The final concentration of KCl present in the assay (~0.5 mM) did not affect the activity of the enzyme. One unit of enzyme is defined as the amount of enzyme required to produce 1 μmol of product/min at 25°. The inhibition of the enzyme by the antifolates was investigated in a 96 well plate with 200 μl reaction of the above mixture, in the presence of varying concentration of the antifolate[15].
| Molecule ID |
IUPAC (correct names) | Molecular Formula |
% yield | M.P. (°) | IR details | NMR details | FAB-MASS peak (m/e) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 2,4-diamino-6-chloro -[1,3,5] triazine | C3H4ClN5 | 100 | 320 | 3487 (N-H, 1259 (C-N) 799 (C-Cl) | ||||
| S1-1 | 2,4-diamino-6-phenoxy -[1,3,5] triazine | C9H9N5O | 80 | 255-258 | 3395 (N-H), 3057 (Ar-H), | 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, | 328 (M+) | ||
| 2955, 2843 (C-H), 1779 (C=O), | δ, ppm): 6.73 (s, | ||||||||
| 1687, 1550 (C=C), 1356 (C-N), | 4H), 7.36 (s, 2H), | ||||||||
| 1168 (C-O), 857, 770 (OOP) | 7.10-7.17 (m, 3H) | ||||||||
| S1-2 | 2,4-diamino-6-(4-nitro-phenoxy) | C9H8N6O3 | 60 | 290 | 3499 (N-H ),3142 (C-H ) | 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, | |||
| -[1,3,5]triazine | 1338 (C-NO2),1222( O-C ) | δ, ppm): 6.71 (s, | |||||||
| 4H), 2.24 (s, 3H), | |||||||||
| 6.84-6.89 (d, 2H), | |||||||||
| 2.01 (s, 3H), 7.09 (s, 1H) | |||||||||
| S1-3 | 2,4-diamino-6-(4-chloro-phenoxy) | C9H8ClN5O | 50 | 280 | 3506 (N-H),3144 (C-H) | ||||
| -[1,3,5]triazine | 1205 (O-C),779 (C-Cl) | ||||||||
| S1-6 | 2,4-diamino- 6-(4-methoxy | C10H11N5O</2 | 60 | 246 | 3493 (N-H),3005 (C-H ) | ||||
| -phenoxy) -[1,3,5]triazine | 2837 (C-H),1251 (O-C) | ||||||||
| 1182 (O-C) | |||||||||
| S1-9 | 2,4-diamino-6-(2,5-dimethyl -phenoxy) -[1,3,5]triazine | C 11 H 13 N5 O | 68 | 255 | 3518 (N-H),2854 (C-H) | 1H NMR (DMSO-d 6, | |||
| 1226 (O-C) | δ, pm): 6.71 (s, | ||||||||
| 4H), 2.24 (s, 3H), | |||||||||
| 6.84-6.89 (db, 2H), | |||||||||
| 2.01 (s, 3H), 7.09 (s, 1H) | |||||||||
| S1-4 | 2,4-diamino-6-(2-chloro | C9H8ClN5O | 48 | 284 | 3522(N-H),3009(C–H) | ||||
| -phenoxy) -[1,3,5]triazine | 2854(C-H),1192(O-C) | ||||||||
| S1-7 | 2,4-diamino-6-(naphthalen-2 | C13H11N5O | 55 | 298 | 3369(N-H),2934(C–H) | 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, | |||
| -yloxy) -[1,3,5]triazine | 1277(O-C) | δ, ppm): 6.74 (s, | |||||||
| 4H), 7.91 (s, 3H), | |||||||||
| 7.30-7.64 (m, 4H) | |||||||||
| S1-15 | 2,4-diamino-6-(biphenyl-4-yloxy) | C15H13N5O | 32 | 274 | 3466(N-H),740(C–H) | 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, δ, | |||
| -[1,3,5]triazine | 1224(O-C–H) | ppm): 6.87 (s, 4H), | |||||||
| 7.73-7.74 (m, 4H) | |||||||||
Table 2: Synthetic And Spectral Details Of The Molecules Synthesized
Results and Discussion
It has been established that Plasmodium falciparum acquires resistance against the antifolates by mutation of residues in the active pocket. Such mutations lead to ‘expulsion’ of the molecules from the active pocket causing a drastic decrease in their affinity and consequently antimalarial activity. A great deal of effort is underway to find solutions to this problem. The abstract of all such efforts is the design of molecules that exploit interactions with different sets of residues in regions of the active site and to incorporate flexibility into the molecules so as to avoid the repulsive forces that cause them to be expelled from the active site. With both these considerations in mind, the design of triazino analogues was taken up.
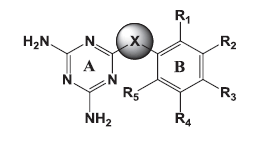 |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule | X | Ring B | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | Conc.in µM | %Inhibition | |
| WT | MT | |||||||||
| S1-1 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -H | -H | -H | 500 | 14.4 | 1.6 |
| S1-2 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -NO2 | -H | -H | 50 | 9.6 | 3.9 |
| S1-3 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -Cl | -H | -H | 500 | 33.8 | 2.6 |
| S1-4 | -O- | Phenyl | -Cl | -H | -H | -H | -H | 100 | 7 | 3.5 |
| S1-6 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -OCH3 | -H | -H | 500 | 17.8 | 8.7 |
| S1-7 | -O- | α- | - | - | - | - | - | 500 | 39.8 | 2.2 |
| Naphthyl | ||||||||||
| S1-9 | -O- | Phenyl | -CH3 | -H | -H | -CH3-H | 100 | 19.2 | 5 | |
| S1-10 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -CH3 | -H | -CH3-H | 500 | 12 | 3.7 | |
| S1-11 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -CH3 | -H | -H | -H | 500 | 30.8 | 7.5 |
| S1-15 | -O- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -Phenyl | -H | -H | 500 | 48.6 | 0.5 |
| S3-1 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -H | -H | -H | 50 | 40.3 | 12.3 |
| S3-2 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -NO2 | -H | -H | 50 | 27.1 | 7.3 |
| S3-3 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -Cl | -H | -H | 50 | 25.4 | 6.4 |
| S3-9 | -NH- | Phenyl | -H | -H | -CH3 | -H | -H | 500 | 48.3 | 3.9 |
| S3-42 | -NH- | Phenyl | -Cl | -H | -Cl | -H | -H | 500 | 28.8 | 0.1 |
| WT=Wild type, MT=mutant type | ||||||||||
Table 3: Biological Activity Of Molecules Against Pf Dhfr Of Wild And Mutant Strains
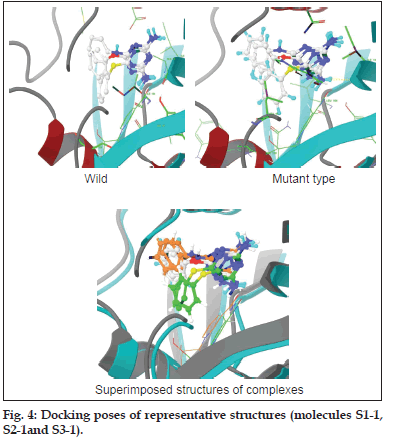
The molecules designed using virtual screening and molecular modelling techniques have docking scores (GoldScore) in the range of 36–57 units, which are comparable with the scores for PYR as the standard (51.56 for wild type and 54.02 for the mutant type strain) (fig. 4). The CoMFA model helped to reveal substitution patterns that best suit the requirements in the active pocket. With the statistics exhibited in Table 4 it must be believed that the models obtained are robust and can confidently be used in any design strategy. As mentioned earlier, the models were validated internally as well as externally. The six models presented in Table 4 are the best of several models built with different parameters and settings. As for the ability of the models to predict the activity of molecules outside the training set is limited, as evidenced by the values of their regression coefficient (p2) for the external dataset, that is test set. Only model 3 seems to be satisfactory for predicting the activity of molecules against the wild type, while for the tetramutant species, model 5 seems to be best suited. The activity predicted by the 3D−QSAR models is in track with the experimental observations (Table 5).
| Model | Wild | Tetra-mutant | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | ||
| C | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| n | 20 | 25 | 30 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
| q2 | 0.42 | 0.59 | 0.48 | 0.68 | 0.48 | 0.42 | |
| r2 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| p2 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.56 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 0.16 | |
| r2cv | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 0.48 | 0.43 | |
| b2 | 0.998±0.001 | 0.998±0.002 | 0.996±0.002 | 0.999±0.001 | 0.992±0.008 | 0.993±0.006 | |
| SE | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.08 | |
| F | 579.95 | 91.38 | 782.59 | 1496.98 | 129.13 | 278.69 | |
| % Contribution | |||||||
| Steric | 0.83 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.87 | |
| Electrostatic | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.13 | |
Table 4: Statistical Data Of The 3d -Qsar Models.
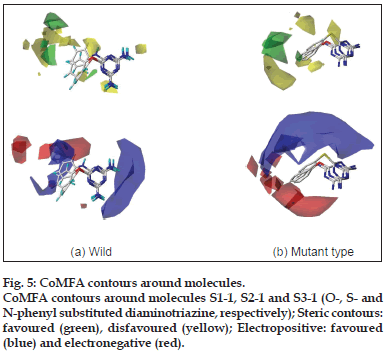
The CoMFA steric contours are more prominent than the electrostatic ones and can explain more of the variation in the biological activity of the molecules. The CoMFA contours (fig. 5) were analysed around molecules S1−1, S2−1 and S3−1, which are representatives of the three series of molecules synthesised. The steric contours indicate that the bulky groups cannot be directly attached to any position on the two rings (A and B, Table 1) but the group must be spaced out through use of a long linker. It was observed from the docking studies that molecules in all the three series are buried deep in the active pocket and thus there is ample scope for further substitutions on these molecules. It is also apparent from the pattern of the contours, that for the wild type enzyme, substituents with some degree of flexibility can be accommodated, while in case of the tetramutants, the substituents need to be directed in a specific orientation. There is a strict prohibition (yellow contours) to steric bulk on the diamino group and heteroatom linker indicates that there is no space in the receptor cavity to accommodate any further substitution.
| Molecules | Wild | Tetra-mutant | Molecules | Wild | Tetra-mutant | Molecules | Wild Tetra-mutant | Molecules | Wild | Tetra-mutant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 3 | Model 5 | Model 3 | Model 5 | Model 3 | Model 5 | Model 3 | Model 5 | ||||
| S1-1 | 7.9 | 5.31 | S1-34 | 7.91 | 5.28 | 49 | 7.76 | 5.28 | 84 | 8.11 | 5.5 |
| S1-2 | 7.86 | 5.26 | S1-35 | 8.57 | 5.66 | 50 | 7.71 | 5.32 | 85 | 8.09 | 5.41 |
| S1-3 | 7.8 | 5.49 | S2-1 | 7.94 | 5.45 | 51 | 7.68 | 5.34 | 86 | 7.88 | 5.34 |
| S1-4 | 7.95 | 5.29 | S2-2 | 8.46 | 5.74 | 52 | 7.88 | 5.44 | 87 | 7.94 | 5.42 |
| S1-5 | 7.7 | 5.44 | S2-3 | 8.04 | 5.41 | 53 | 8.06 | 5.52 | 88 | 8.04 | 5.37 |
| S1-6 | 7.76 | 5.32 | S2-4 | 8.28 | 5.69 | 54 | 7.99 | 5.31 | 89 | 7.94 | 5.6 |
| S1-7 | 7.88 | 5.42 | S2-5 | 7.92 | 5.35 | 55 | 7.96 | 5.31 | 90 | 7.9 | 4.98 |
| S1-8 | 7.88 | 5.39 | S2-6 | 7.9 | 5.36 | 56 | 7.91 | 5.39 | 91 | 7.7 | 5.46 |
| S1-9 | 7.91 | 5.42 | S2-7 | 7.85 | 5.41 | 57 | 7.86 | 5.31 | 92 | 7.85 | 5.39 |
| S1-10 | 8.01 | 5.41 | S2-8 | 7.8 | 5.39 | 58 | 7.82 | 5.39 | 93 | 8.16 | 5.42 |
| S1-11 | 8.06 | 5.35 | S2-9 | 7.86 | 5.34 | 59 | 7.74 | 5.32 | 94 | 8.06 | 5.66 |
| S1-12 | 8.03 | 5.36 | S2-10 | 7.9 | 5.39 | 60 | 7.89 | 5.36 | 95 | 7.92 | 5.34 |
| S1-13 | 7.94 | 5.28 | S2-11 | 7.82 | 5.43 | 61 | 7.65 | 5.29 | 96 | 8.04 | 5.59 |
| S1-14 | 7.78 | 5.25 | S2-12 | 7.8 | 5.41 | 62 | 7.9 | 5.25 | 97 | 7.85 | 5.07 |
| S1-14 | 7.77 | 5.47 | S2-13 | 7.95 | 5.37 | 63 | 7.79 | 5.34 | 98 | 7.87 | 5.26 |
| S1-15 | 8.08 | 5.77 | S3-22 | 8 | 5.22 | 64 | 7.82 | 5.39 | 118 | 8.22 | 5.43 |
| S1-16 | 8.11 | 5.7 | S3-23 | 7.97 | 5.24 | 65 | 7.98 | 5.42 | 119 | 7.64 | 5.44 |
| S1-17 | 7.9 | 5.39 | S3-24 | 7.94 | 5.18 | 66 | 7.87 | 5.3 | 120 | 7.56 | 5.25 |
| S1-18 | 8.08 | 5.63 | S3-25 | 7.8 | 5.29 | 67 | 7.91 | 5.31 | 121 | 7.66 | 5.38 |
| S1-19 | 7.92 | 5.47 | S3-26 | 8.03 | 5.3 | 68 | 8.05 | 5.92 | 122 | 8.03 | 5.32 |
| S1-20 | 8.05 | 5.35 | S3-27 | 7.77 | 5.33 | 69 | 7.71 | 5.38 | 123 | 7.98 | 5.45 |
| S1-21 | 7.91 | 5.29 | S3-28 | 7.98 | 5.18 | 70 | 7.89 | 5.32 | 124 | 7.95 | 5.29 |
| S1-22 | 7.99 | 5.24 | S3-29 | 7.57 | 5.46 | 71 | 7.86 | 5.45 | 125 | 7.88 | 5.33 |
| S1-23 | 8.03 | 5.3 | S3-30 | 8.23 | 5.04 | 72 | 7.76 | 5.21 | 126 | 7.77 | 5.13 |
| S1-24 | 7.8 | 5.32 | S3-31 | 7.76 | 5.35 | 73 | 8.08 | 5.36 | 127 | 8.26 | 5.36 |
| S1-25 | 7.94 | 5.35 | S3-32 | 8.03 | 5.12 | 74 | 8.28 | 5.8 | 129 | 7.84 | 5.37 |
| S1-26 | 7.81 | 5.4 | S3-33 | 8.08 | 5.3 | 75 | 7.9 | 5.2 | 130 | 8.22 | 5.26 |
| S1-27 | 7.91 | 5.48 | S3-34 | 7.84 | 5.54 | 76 | 8.13 | 5.5 | 131 | 7.87 | 5.19 |
| S1-28 | 8.1 | 5.54 | S3-35 | 7.93 | 5.32 | 77 | 7.86 | 5.46 | 132 | 7.89 | 5.58 |
| S1-29 | 7.91 | 5.39 | S3-36 | 7.8 | 5.25 | 78 | 7.81 | 5.23 | 133 | 7.84 | 5.55 |
| S1-30 | 8.04 | 5.38 | S3-37 | 8.05 | 5.19 | 79 | 7.83 | 5.51 | 134 | 7.84 | 5.75 |
| S1-31 | 8.27 | 5.7 | S3-38 | 7.84 | 5.29 | 80 | 7.72 | 5.29 | 135 | 7.87 | 5.37 |
| S1-32 | 7.8 | 5.38 | S3-40 | 7.54 | 5.47 | 81 | 7.87 | 5.47 | |||
| S1-33 | 8.02 | 5.32 | 82 | 7.82 | 5.46 | ||||||
Table 5: Predicted Pk Values Of Molecules From Series 1, 2 And 3.
In terms of the electrostatic contours, blue contours related to electropositive substituents dominate the electrostatic space on the basic skeleton. The appearance of electropositive contours on the triazine nucleus goes hand−in−hand with the presence of electronegative atoms in the active pocket with the ability to form salt bridges (e.g. with Asp54) and hydrogen bonds (e.g. with Ile14 and Asp54). The electrostatic contours portray a drastic difference in the substitution requirement for the three molecules S1−1, S2−1 and S3−1. For inhibitors of the wild type enzyme, the aromatic ring (B) shows a favour for both electronegative and electropositive substituents. In contrast, inhibitors of the tetramutant species should have strictly electronegative substituents on ring (B).
Some crucial results that emerge from these studies are that a change from a pyrimidine ring to the triazine core increases the binding with pfDHFR. Contributors to the additional binding are H−bond interactions between the 2nd and 4th amino groups of triazine with the COO− group of Asp54, the backbone carbonyl group of Ile14, and the hydroxyl group of Tyr170. Molecules with the triazine ring linked through a ethers/thioether group to aromatic or an aliphatic ring with fewer than six atoms (i.e. furan, cyclopentane) have poor binding affinity compared with six membered rings like pyridine.
The molecules were synthesised by combining 2,4−diamino−6−chloro−1,3,5−triazine− (II) with substituted phenols or thiophenols or anilines in presence of acetone. It was observed that reactions with phenols containing electron withdrawing groups needed longer reaction times than phenols with electron donating substituents. Also the final condensation reaction needs to be carried out in solvents having boiling points above 90°. The reactions were also carried out using a parallel synthesiser to improve the yield, purity and reaction time, however, no significant changes were observed for series 1 and 2 while an increment in the yield (from 60% to 80%) was observed for molecules of series 3.
Amongst the synthesised molecules, ten compounds (Table 3) were initially tested against pfDHFR. Compounds with electron donating groups on the 6−phenyl ring inhibited the activity at about 500 μM concentrations, those with bulky groups on the 6−phenyl ring at 100 μM and those with electron withdrawing group at 50 μM concentrations (Table 3).
From the inhibition pattern it was concluded that molecules with an alkyl substitution on the phenyl ring, for example molecule (S1−10), are more potent on the wild type rather than on the tetramutant strain. Groups like −NO2 and −Cl on the phenyl ring, for example molecules S3−2 and S3−3, S3−42 with the NH linker potentiate activity on the wild rather than on the mutant strain while the same groups on molecules with −O− as the linker (molecules S1−2, S1−3 and S1−4) confer low activity against both wild and mutant strains. Among the molecules of series 3, the most active molecule was one without substitution on the phenyl ring linked through NH linker group, that is molecule S3−1 showed 40.3% inhibition against wild type plasmodium at 50 μM concentration. The moderately active molecules S1−15 and S3−9 in this series have groups such as phenyl and methyl, respectively, on the ring B (phenyl ring 3rd position) with O and NH groups as linkers, respectively. This is probably due to increased hydrophobic interaction with the nonpolar residues in the pocket. As far as activity against mutant species is concerned, the mutation have altered the placement of the molecules S3−1 and S3−9 significantly while S1−15 owing to better hydrophobic interaction exhibited better docking score yet it exhibited even lesser activity than the other two.
Chemotherapy with antifolates remains the most important means of controlling malaria. The structure of the active site of the enzyme reveals that the essential determinants for tight binding are (a) heterocyclic ring (b) hydrogen bond acceptor/donor functional groups capable of hydrogen bonding and (c) nonpolar functional groups that fit into the hydrophobic core of the active site. All these aspects were taken cognisance of in the design of molecules reported in this paper. A similar type of work was reported by Morgan et al., which revealed that the series of 2,4−pyrimidines substitution at 4th position of pyrimidine nucleus with NH linker diminishes the antimalarial activity[16]. Hence triaminotriazine nucleus was used in place of diaminopyrimidine to identify newer inhibitors. The increasing rate of resistance has been observed against drugs like PYR and CYG due to mutation in pfDHFR. The basic cause behind resistance being the steric repulsion to these drugs, an initiative was taken to design and synthesise new molecules with higher flexibility. The idea of increasing flexibility in new inhibitors was taken from observation of a novel molecule WR99210 and incorporated in TMP core to make its congeners. The synthesis was achieved using well established procedures and the structures fully characterised by spectroscopic techniques. Molecules were evaluated for pfDHFR inhibition and found to be moderately active against wild type strain and inactive against mutant strains. There is thus a need to reengineer the structures of these compounds so as to improve their activity against wild type and in particular the mutant strain. In this context, there exists ample scope for improvement in the design and the CoMFA models will be used to guide the design of newer analogues that will be taken up in the near future.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to National Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, National Science and Technology Development Agency, Thailand for carrying out bioassays. PKA and RRP thanks the All India Council of Technical Education (8023/BOR/RID/RPS−181/2009−12), CSIR (02 (0047)/12/EMR−II/2012−15) and the University of Mumbai for financial support (APD/237/157/20th Nov. 2010). ECC thanks the Department of Science and Technology for the infrastructure facilities through the FIST program (SR/FST/LS1−163/2003) CSIR (01/(2399)/10/ EMR−II) and DBT (BT/PR11810/BRB/10/690/2009).
References
- Amina K, Giuliana G, Prato M. From control to eradication of malaria: The end of being stuck in second gear? Asian Pac J Trop Med 2010;3:412-20.
- Chiang PK, Bujnicki JM, Su X, Lanar DE. Malaria: Therapy, genes and vaccines. CurrMol Med 2006;6:309-26.
- Toyoda T, Brobey RK, Sano G, Horii T, Tomioka N, Itai A. Lead discovery of inhibitors of the dihydrofolatereductase domain of Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolatereductase-thymidylate synthase. BiochemBiophys Res Commun 1997;235:515-19.
- Canfield CJ, Milhous WK, Ager AL, Rossan RN, Sweeney TR, Lewis NJ, et al. Ps-15: A potent, orally active antimalarial from a new class of folic acid antagonists. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1993;49:121-6.
- Edstein MD, Kotecka BM, Ager AL, Smith KS, DiTusa CA, Diaz DS, et al. Antimalarial pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of a third-generation antifolate--JPC2056--in cynomolgus monkeys using an in vivo in vitro model. J AntimicrobChemother 2007;60:811-8.
- Sybyl. 1699 S Hanley Rd., St. Louis, MO 631444, USA, Tripos Associates Inc., 2005.
- Cramer RD 3rd, Patterson DE, Bunce JD.Comparative molecular field analysis (comfa). I. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am ChemSoc 1988;110:5959-67.
- Cramer RD 3rd, Patterson DE, Bunce JD. Recent advances in comparative molecular field analysis (comfa). ProgClinBiol Res 1989;291:161-5.
- Gold, Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC), UK, 2005.
- Sirichaiwat C, Intaraudom C, Kamchonwongpaisan S, Vanichtanankul J, Thebtaranonth Y, Yuthavong Y. Target guided synthesis of 5-benzyl-2,4-diamonopyrimidines: Their antimalarial activities and binding affinities to wild type and mutant dihydrofolatereductases from plasmodium falciparum. J Med Chem 2004;47:345-54.
- Yuvaniyama J, Chitnumsub P, Kamchonwongpaisan S, Vanichtanankul J, Sirawaraporn W, Taylor P, et al. Insights into antifolate resistance from malarial dhfr-ts structures. Nat StructBiol2003;10:357-65.
- Accelrys I. Insight II. San Diego, CA, USA, 2005.
- Adams P, Kaiser D, Nagy D, Peters G, Sperry R, Thurston J. Chemistry of dicyandiamide. Ii. Preparation and hydrolysis of acyldicyandiamides. J Org Chem 1952;17:1162-71.
- Kaiser DW, Thurston JT, Dudley JR, Schaefer FC, Hechenbleikner I, Holm-Hansen D. Cyanuric chloride derivatives. II. Substituted melamines. J Am ChemSoc 1951;73:2984-6.
- Sirawaraporn W, Prapunwattana P, Sirawaraporn R, Yuthavong Y, Santi DV. The dihydrofolatereductase domain of plasmodium falciparum thymidylate synthase-dihydrofolatereductase.Gene synthesis, expression, and anti-folate-resistant mutants. J BiolChem 1993;268:21637-44.
- Morgan J, Haritakul R, Keller P. Antimalarial activity of 2, 4-diaminopyrimidines. Lett Drug Des Discov 2008;5:277-80.