- *Corresponding Author:
- Chunzhu Zhang
Department of Medical Imageology, Beijing Rehabilitation Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing 100144, China
E-mail: 3216198402@qq.com
| This article was originally published in a special issue: Special issue on “Animal Models & Experimental Medicine” |
| Indian J Pharm Sci 2020:82(1) spl issue4;56-60 |
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms
Abstract
To evaluate the rehabilitation conditions of Parkinson’s disease patients using combined therapy of Bushenzhichan formula and needle embedding and to analyze the magnetic resonance imaging test results, 180 Parkinson’s disease patients treated at the Beijing Rehabilitation Hospital of Capital Medical University were enrolled as research subjects. They were randomly divided into the control group and the research group, each containing 90 patients. The research group was treated with Madopar as well as the combined therapy of Bushenzhichan formula and needle embedding, while the control group received only Madopar. The rehabilitation conditions of both groups were compared. The total therapeutic efficacy of the research group was higher than that of the control group. By comparing the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale I, scale II and scale III scores, after treatment, the research group showed more significant improvement than the control group. Moreover, magnetic resonance imaging results showed low signal intensity in the red nucleus and substantia nigra. There was no significant difference in the volume of red nucleus and substantia nigra between the two groups. The combined therapy of Bushenzhichan formula and needle embedding can significantly improve the therapeutic efficacy and promote recovery of Parkinson disease patients.
Keywords
Bushenzhichan formula, Needle embedding, Parkinson’s disease, Rehabilitation, MRI results
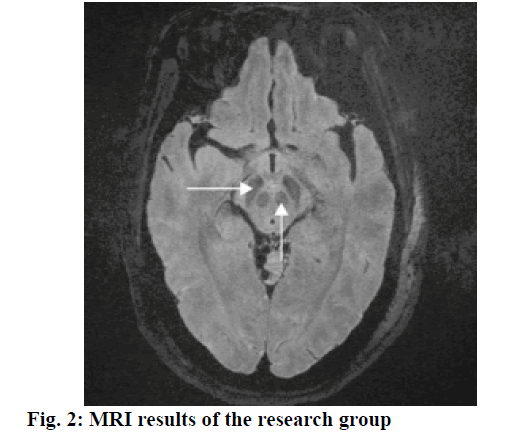
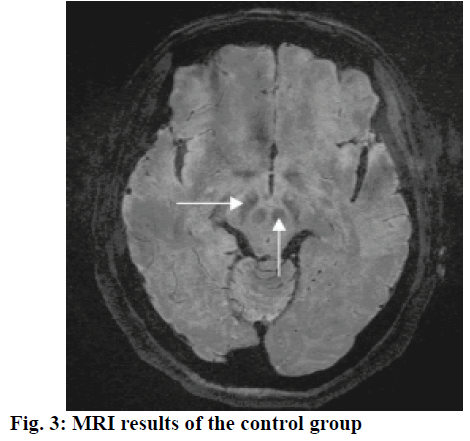
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common disease among the middle-aged and elderly population, which is mainly characterized by motor symptoms such as tremor, muscle rigidity, bradykinesia and posture instability as well as non-motor symptoms such as hyposmia, constipation and depression[1,2]. With the aggravation of the aging society, the number of people suffering from Parkinson disease is increasing, which has attracted considerable concern in clinical medicine. It has been reported that approximately 90 % of PD cases are primary PD, while others are secondary PD syndromes, genetic degeneration Parkinson’s syndrome and Parkinson’s superposition syndrome[3-5]. Numerous factors contribute to PD, which are genetic, environmental toxins, immunoinflammatory mechanisms and so on. Currently, there is still a lack of effective treatment for PD. Thus, it is of great importance to explore more effective treatments and drugs. In this study, the rehabilitation conditions of PD patients treated with combined therapy of Bushenzhichan formula and needle embedding were evaluated and their MRI test results were analyzed. One hundred and eighty PD patients, who had been treated at the Beijing Rehabilitation Hospital of Capital Medical University from June 2015 to June 2018 were enrolled as research subjects. The patients’ images are shown in fig. 1. All cases met the diagnostic criteria made by the Motor Disorder and Parkinson’s Disease Group of the Chinese Medical Association Neurology Chapter. Meanwhile, the criteria for diagnosis and curative effect evaluation of senile tremor syndrome in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) made by China Association of Chinese Medicine were taken as reference for diagnosis in Chinese Medicine[6,7]. Patients were randomized into the research group and the control group, each containing 90. The research group contained 50 male and 40 female patients with age ranging from 52 to 79 y and a median age of 67.4±3.3 y. The average course of disease of this group was 8.6±0.9 y, ranging from 1 to 14 y. In contrast, the control group contained 56 male and 34 female patients, with the age ranging from 54 to 80 y, and the median age was 68.2±3.6 y. The average course of disease was 7.2±0.5 y, ranging from 1 to 6 y. Data obtained from both the groups were comparable (P>0.05). The patients in the control group was treated with Madopar, 125-1250 mg, 3-4 times a day. Based on that regimen, patients in the research group were treated with a combined therapy of Bushenzhichan formula and needle embedding. Of those, Bushenzhichan formula is formed with modified combination of Guilu Erxian ointment and DadingFengzhu. The constituents of Bushenzhichan formula are as follows, 9 g deer antler glue, 9 g Zhigancao, 20 g raw tortoise plastron, 20 g fructus cannabis, 20 g codonopsis, 20 g raw turtle shell, 12 g gelatin, 12 g gastrodiaelata, 12 g pulp of cornus, 30 g fractus lycii, 30 g Radix paeoniae alba, 30 g dried Radix rehmanniae, 30 g cistanche, 30 g uncaria, 15 g Radix ophiopogonis and 10 g polygonatum. It is a single Chinese herb free from decotion, which could be dissolved in 400 ml of boiled water, once a day and used as a tea after lunch and dinner while warm. The prescription of needle embedding is listed as follows, Baihui, Sishencong, Fengchi, Taichong, Yanglingquan, Sanyinjiao, Hegu, Ganshu, Shenshu and the chorea-trembling controlled area. The needle embedding procedure is, pushpin-type sterile sputum needles were used (Suzhou Hualun Medical Products Co., Ltd., Batch number: 11101). The embedding area skin and the forceps were disinfected, the needle ring was clamped with the force and the needle tip punctured at each acupuncture point. The annular needle handle is placed on the skin and fixed with a tape and the needle tip was left intact for a day in summer, or for 3 d in winter. During the indwelling process, the needle was pressed for 2 min every day to enhance stimulation and increase therapeutic efficacy. Madopar (Shanghai Roche Pharmaceutical Company, Batch number: SH1324) was administered at a dosage of 125- 1500 mg/d, 3-4 times a day. Both groups were treated continuously for 4 w, as a course of treatment and the therapeutic effects after 3 complete courses of treatment were statistically analyzed. The total therapeutic efficacy was observed and compared between both groups. According to Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), if the total scores decreased more than 30 % after treatment, it was regarded as excellent, if the total scores decreased in the range of 5 to 29 % after treatment, it was regarded as valid, if the total scores decreased less than 5 % after treatment, it was regarded as invalid treatment. Moreover, UPDRS I, II and UPDRs III scores were recorded. SPSS21.0 software was used to perform statistical analyses. The quantitative data were expressed as mean±standard dviation, with t-test for intergroup comparison. Enumeration data are expressed as natural number (n) and percent (%), with chi-square test for intergroup comparison. The difference was considered statistical significant when P<0.05. It can be seen from Table 1 that the total therapeutic efficacy of the research group was significantly higher than that of control group (P<0.05). On comparing the UPDRS I scores of the 2 groups it was observed that the score of the research group was significantly reduced after each course of treatment (P<0.05), as shown in Tables 2 and 3. On Comparing the UPDRS II and III scores and the total scores of both the groups. The scores of the research group were significantly decreased after treatment P<0.05). When the volume of red nucleus and substantia nigra as obtained from MRI data of patients was compared between both the groups low signal intensity of the red nucleus and substantia nigra were observed in layer 12-22 and layer 25-34, respectively as shown in figs. 2 and 3. The volume and the standardized volume of red nucleus and substantia nigra between both groups were not significantly different (P>0.05). As a common neurodegenerative disease threatening both mental and physical health in the middle-aged and elderly population, PD has aroused much concerns. According to the Chinese medicine, PD falls into the category of tremor and vibration. It has been clearly elaborated in Su wen that the core of this disease is exhaustion of the essence and blood and water failing to moisten wood…the liver yang is rather high, sometimes with endogenous wind[8-10]. Therefore, the disease is mostly caused by long-term illness or kidney deficiency in elderly, dysregulation of absorption, compromised kidney essence, or the homogeny of liver and kidney. In this study, the therapeutic effect of combined therapy of Bushenzhichan formula and needle embedding were observed among PD patients, from the theory of liver and kidney[11-14]. Bushenzhichan formula is a modified combination of Guilu Erxian ointment and DadingFengzhu. Of those, Guilu Erxian ointment could generate essence, benefit qi, nourish blood and supplement both yin and yang, while the DadingFengzhu could nourish yin and suppress the excessive yang as well as stop endogenous wind. The pulp of cornus, polygonatum, gastrodia elata, uncaria and the like in the formula could nourish kidney and liver as well as stop endogenous wind and tremor. The needle embedding method is mainly characterized as detention to form later meridian inductive effects. The needles were placed in Baihui, Sishencong, Fengchi, Taichong, Yanglingquan, Sanyinjiao, Hegu, Ganshu, Shenshu and the chorea-trembling controlled area, which could nourish kidney and liver as well as stop endogenous wind[15,16]. By combining therapy of both methods, it is possible to nourish both kidney and liver, supplement body essence and marrow as well as stop endogenous wind and tremor. Results of this study showed that the total therapeutic outcome of the research group was higher than that of the control group (P<0.05). After treatment, the UPDRS I, II and III scores of the research group were significantly higher than that of the control group (P<0.05). The above findings fully indicated that the application of the combined therapy of Bushenzhichan formula and needle embedding could produce favorable therapeutic outcome in PD patients. In conclusion, the combined therapy of kidneytonifying antifibrillation and embedding needle is an ideal medical treatment of PD patients. From the perspective of Chinese medicine, PD is caused by chronic disease or aging of the kidney and less sperm loss, together with malabsorption of nutrients, dark exhaustion of the kidney, or homology of liver and kidney and blood. Therefore, the adoption of TCM treatment scheme can give play to the important effect of TCM syndrome differentiation and treatment and conduct targeted treatment for patients. The results of this study are consistent with those of many relevant domestic studies and have strong applicability. Such combined therapy could promote the recovery of patients as soon as possible, which is worth a lot of promotion and application. In the current society, the therapeutic effect of patients is not only reflected in physical recovery, but also the content of life quality, including psychological function and social function. Therefore, future studies need to pay attention to the effect of combined therapy of kidney-nourishing antifibrillation formula and embedding needle on the quality of life of PD patients.
| Groups | cases | Excellent | Valid | Invalid | Total therapeutic efficacy, n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research group | 90 | 66 | 20 | 4 | 86 (95.56) |
| Control group | 90 | 21 | 50 | 19 | 71 (78.89) |
| t | 12.20 | ||||
| P | < 0.05 |
Table 1: Comparison of the Total Therapeutic Efficacy between both Groups
| Group | Before treatment | After 1 course of treatment | After 2 courses of treatment | After 3 courses of treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research group (n=90) |
2.58±1.80 | 1.66±0.37 | 1.30±0.93 | 1.22±0.68 |
| Control group (n=90) |
2.50±1.73 | 2.25±1.40 | 2.22±1.02 | 2.21±1.36 |
| t | 0.49 | 5.21 | 9.35 | 6.33 |
| P | > 0.05 | < 0.05 | < 0.05 | < 0.05 |
Table 2: Comparison of the Updrs I Scores between both Groups
| Groups | Time | UPDRS II scores | UPDRS III scores | Total scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research group (n=90) |
Before treatment | 14.22±5.19 | 35.50±10.28 | 52.17±20.15 |
| After 3 courses of treatment | 10.93±4.92 | 30.29±11.28 | 42.18±14.39 | |
| Control group (n=90) |
Before treatment | 14.60±6.09 | 35.26±11.25 | 52.18±19.04 |
| After 3 courses of treatment | 13.92±4.39 | 33.28±10.36 | 51.07±18.27 |
Table 3: Comparison of the Updrs Ii, Iii and Total Scores between Two Groups
References
- Hu YY, Chen W. Effects of combined therapy of Bushenzhichan Formula and needle embedding on the expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in Parkinson’s disease mice model. Chinese J Gerontol 2015; 35(05):1341-3.
- Cao SW, Zhao CS, Hong XN. Application of image fusion technology in deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Chinese J Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 2015;28(03):134-7.
- Hu YY, Huang H, Song ZL. Effects of combined therapy of Bushenzhichan Formula and needle embedding on the expression of TH and GFAP in Parkinson’s disease rat model. Chinese J Integ Med Cardio Dis 2017;15(03):305-9.
- Iwata H, Masuda N, Ohno S. A randomized, double-blind, controlled study of exemestane versus anastrozole for the first-line treatment of postmenopausal Japanese women with hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2016;139(2):441-51.
- Lee DS, Kim SH, Kim S. Prognostic significance of breast cancer subtype and p53 overexpression in patients with locally advanced or high-risk breast cancer treated using upfront modified radical mastectomy with or without post-mastectomy radiation therapy. Int J Clin Oncol 2017,17(5):447-55.
- Wang XZ, Qian M, Xie M. Clinical Research Progress in Traditional Chinese Medicines Combined with Dopa Preparations in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. China Pharmacist 2017;20(09):1578-83.
- Mo HZ, Hu YY, Liang HH. Clinical study on Parkinson’s disease with depression with yin deficiency of liver and kidney by the therapy of Yishen Tiaogan Jieyu. Tianjin J Trad Chinese Med 2018;35(01):11-4.
- Danishada KKA, Sharmaa U, Saha RG. Assessment of therapeutic response of locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) monitored using sequential magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI). NMR Biomed 2017;23(3):233-41.
- Sharma U, Danishad KKA, Seenu V. Longitudinal study of the assessment by MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging of tumor response in patients with locally advanced breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. NMR Biomed 2017;22(1):104-13.
- Fei F, Chen C, Xue J. Efficacy and safety of docetaxel combined with oxaliplatin as a neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen for Chinese triple-negative local advanced breast cancer patients: A prospective, open, and unicentric phase II clinical trial. Am J Clin Oncol 2018;36(6):545-51.
- Ge S, Liu Z, Furuta Y. Characteristics of activated carbon remove sulfur particles against smog. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2017;24(6):1370-4.
- Liu Y, Li T, Guo L. The mediating role of sleep quality on the relationship between perceived stress and depression among the elderly in urban communities: a cross-sectional study. Public Health 2017;149:21-7.
- Gao W, Wang Y, Wang W. The first multiplication atom-bond connectivity index of molecular structures in drugs. Saudi Pharm J 2017;25(4):548-55.
- Vural M, Mert M, Erhan B. Is there any relationship between mean platelet volume, bone mineral density and vitamin d in postmenopausal women? Acta Medica Mediterr 2017;33(3):443-8.
- Chawla S, Agarwal M, Sharma S. Drug utilization study of psychotropic drugs among psychiatric outpatients in a tertiary care hospital. Indian J Pharm Sci 2017;79(6):1008.
- Tezer MS, Gilan IY, Elvan O. Topographic methods to exposethe exiting points of supratrochlear, supraorbital, and zygomaticotemporal nerves. Turk J Med Sci 2017;47(6):1861-5.