- *Corresponding Author:
- Y. Yang
Department of Emergency Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, No. 20, Xisi Road, Nantong, Jiangsu 226001, China
E-mail: Yangyang286228@163.com
| This article was originally published in a special issue, “Evolutionary Strategies in Biomedical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences” |
| Indian J Pharm Sci 2021:83(3) Spl issue;109-113 |
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms
Abstract
To explore the effects of psychological nursing based on management by objectives on health behaviors and family satisfaction of pediatric inpatients. 82 cases of children admitted to our hospital from January 2019 to January 2020 were selected. All children were divided into the observation group (n=41) and the control group (n=41) according to random number method. Patients in the control group were given routine care and patients in the observation group were given management by objectives based psychological nursing. After nursing, the nursing quality of the two groups and the psychological state of the patients were compared. The Omaha outcome scale was used to compare the health behaviors between the two groups. The nursing satisfaction of the two groups of patient’s family members was compared with the scale made by our hospital. Compared with the control group, the nursing quality of the observation group was significantly increased (p<0.05). The total incidence of separation anxiety, loss of control and pain reaction in observation group was significantly lower than that in control group (p<0.05). Compared with the control group, the nutritional score, rest score and activity score in observation group were significantly increased after nursing (p<0.05). The satisfaction of family members with nursing in the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group (p<0.05). Management by objectives based psychological nursing has a significant application value in pediatrics, which can significantly improve the health behavior of patients, improve the nursing satisfaction of patient’s families. Thus, it is worthy of further clinical promotion and application.
Keywords
Management by objectives, psychological nursing, pediatrics, health behavior, nursing satisfaction, application value
With the continuous development of social economy, education level and medical technology, people’s requirements for nursing are getting higher[1]. Especially in pediatric nursing, parents pay more attention to children’s nursing. In pediatrics, there are many common diseases for those children are younger and emotionally unstable and children’s expression ability is poor. In the process of pediatric nursing, not only children’s emotions should be paid attention to, but also parents mood[2]. Therefore, the requirements for medical services will also increase. A little neglect will lead to medical disputes and aggravate the tension between doctors and patients[3]. Children belong to a more specific group, whose acceptance ability, communication ability and cooperation ability are poor, so it needs a strong sense of responsibility in the nursing of pediatrics. Nursing staff need patience, love and compassion in the nursing of pediatrics. In addition to basic operations, psychological nursing also plays a key role in the nursing of children[4]. In recent years, the concept of management by objectives (MBO) has been widely used in nursing measures. Its core concept is to carry out corresponding work on the basis of establishing objectives. First, the overall objectives are established, then reasonable decomposition is carried out and it is converted into individual objectives. The organization evaluates and rewards and punishments according to the completion of the decomposed objectives[5]. Previous clinical studies have shown that, the concept of MBO conforms to the trend of modern development, which can significantly improve the enthusiasm of nursing staff, improve nursing quality and provide patients with a better nursing model[6]. Therefore, this article will explore the influence of psychological nursing based on MBO on the health behavior and family satisfaction of pediatric inpatients, aiming at providing a reference basis for the choice of clinical pediatric nursing methods.
Materials and Methods
General data:
A total of 82 children admitted to our hospital from January 2019 to January 2020 were selected, including 42 males and 40 females. The age of patients ranged from 1 to 11 y old, with an average age of 5.95±0.59 y old. Family members aged from 25 to 55 y old, with an average age of 40.16±2.01 y old. Among them, there were 13 cases of respiratory diseases, 15 cases of urinary system diseases, 10 cases of cardiovascular diseases, 16 cases of blood system diseases and 28 cases of nervous system diseases. According to random number method, all children were divided into the observation group and the control group, with 41 cases in each group, including 20 males and 21 females in observation group, with an average age of 5.96±0.18 y old. There were 22 males and 19 females in the control group, with an average age of 5.89±0.67 y old. All children and their families were aware of this study and have signed informed consent forms.
Inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria:
Inclusion criteria: Patients with complete clinical data; patients with no serious organ injury or malignant tumor; patients who can be followed up; patients who can cooperate with this researcher continuously.
Exclusion criteria: Patients with severe autoimmune diseases; patients who are not aged between 1 and 11 y old; patients whose parents are not aware of this study.
Nursing methods:
Routine nursing was given to children in the control group, which mainly included: health education and publicity for children and their families, guiding children’s medication, diet, precautions and living habits, etc., and keeping the ward clean and comfortable.Routine nursing was given to children in the control group, which mainly included: health education and publicity for children and their families, guiding children’s medication, diet, precautions and living habits, etc., and keeping the ward clean and comfortable.
The observation group received MBO based psychological nursing on the basis of the control group. Its main contents are as follows:
To establish a MBO group: The group members are composed of an experienced head nurse and five nurses. The five nurses are responsible for the specific implementation of MBO based psychological nursing and all of them are trained before nursing.
To formulate management objectives: The head nurse shall lead the nurses to get a comprehensive understanding of the clinical data of the patients, register the condition, clinical manifestations and treatment of the children and establish personal files and communicate with the parents of the children to fully understand the condition of the children and formulate nursing goals and plans in combination with the basic situation of the children.
Psychological nursing strategy: Nursing of children; nursing staff should take care of children according to their psychological characteristics. Due to the younger age of the child, it is prone to emotional swings and is affected by the external environment. Moreover, due to the influence of diseases, the quality of life of the child is significantly reduced and physical discomfort will cause difficulties in communicating with the child. At this time, nursing staff should be patient in communicating with the child and cannot reprimand the child, which is easy to cause the child to wail aloud and the dissatisfaction of parents. For children receiving intravenous infusion, the blood vessels are relatively thin, the puncture is difficult and the cooperation degree of the children is low and the ability to tolerate pain is also poor. At this time, the nursing staff should communicate with the family members of the children to appease the children’s emotions and communicate with the children to divert their attention. Parents should cooperate with the nursing staff more to achieve the expected goal. For children who are extremely uncooperative, they should actively communicate with them, find out the reasons, listen patiently to their feelings, answer their questions in a gentle tone and eliminate their bad emotions. For some older children, some have rebellious psychology. Therefore, nursing should be carried out in combination with the actual mood and state of children. At this time, children are psychologically sensitive. The tone should be gentle when nursing. Gentle attitude and nursing according to children’s emotions, understanding the degree of dysphoria of children in the process of communication with children, understanding their psychological needs and trying their best to meet the needs, encouraging children in the process of nursing, so that children’s negative emotions can be relieved and facing them with the mentality of children’s friends, so as to successfully complete nursing and improve nursing quality. Nursing for parents of children: Nursing staff should treat parents of children with a friendly and positive attitude, introduce the development of children’s diseases and treatment methods to parents of children, improve their understanding of diseases and help parents of children to cooperate with the implementation of nursing. In addition, nursing staff should understand the eager mood of the parents of the children, appease their psychology in a timely manner and try to meet the requirements of the parents of the children, carry out more empathy and teach parents some nursing skills to jointly help the children overcome the disease.
Nursing quality: The nursing quality of the two groups of patients was evaluated and compared with the selfmade survey scale in our hospital. The nursing quality includes three grades: excellent, good and poor and the nursing effective rate=(excellent+good)/total number of cases.
Psychological state: The incidence of separation, anxiety, loss of control and pain reaction in the two groups were statistically compared by using Hamilton anxiety scale, loss of control response scale and pain response scale, respectively after nursing.
Health behavior: The health behavior of the two groups of children was compared and the Omaha outcome was used to evaluate the health behavior of the two groups of children. The health behavior includes nutrition, rest and activity, the higher the score of the patient, the better the health behavior.
Satisfaction of family members of children: The satisfaction of family members of children in the two groups was compared. The satisfaction was divided into very satisfied, satisfied and dissatisfied. Satisfaction rate=(very satisfied+satisfied)/total number of cases.
Statistical analysis:
SPSS 22.0 statistical software was used to analyze the data. The measurement data conforming to normal distribution were expressed as mean±standard deviation (x̄±s) and the comparison between groups was conducted by t test; counting data were expressed as the number of cases (n) or percentage (%) and the data comparison was tested by χ2 test. When p<0.05, the difference was statistically significant.
Results and Discussion
Comparison of general data between the two groups; there were no significant differences in gender, average age, body mass index (BMI) and disease type between the two groups (p>0.05), as shown in Table 1.
| Group | Observation group (n=41) | Control group (n=41) | Statistical value | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (cases) | ||||
| Male | 20 | 21 | 5.267 | 0.492 |
| Female | 22 | 19 | ||
| Mean age (years old) | 5.96±0.18 | 5.89±0.67 | 4.269 | 1.003 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.14±2.66 | 20.32±2.49 | 4.198 | 0.129 |
| Type of disease | ||||
| Respiratory diseases | 6 | 7 | 3.297 | 0.268 |
| Urinary system diseases | 8 | 7 | ||
| Cardiovascular disease | 5 | 5 | ||
| Diseases of the blood system | 8 | 8 | ||
| Diseases of nervous system | 14 | 14 |
Table 1: Comparison of General Data between the Two Groups
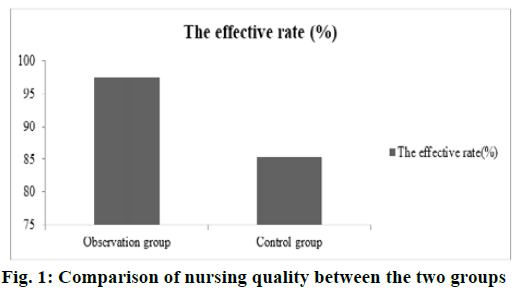
Comparison of nursing quality between the two groups; the nursing effective rate of children in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group and the difference was statistically significant (p<0.05), as shown in Table 2 and fig. 1.
| Group | Observation group (n=41) | Control group (n=41) | χ2 | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excellent | 20 (48.78) | 18 (43.90) | - | - |
| Good | 20 (48.78) | 17 (41.46) | - | - |
| Poor | 1 (2.43) | 6 (14.63) | - | - |
| Efficiency | 40 (97.57) | 35 (85.36) | 5.124 | 0.008 |
Table 2: Comparison of Nursing Quality between the Two Groups [N(%)]
Comparison of mental states between the two groups of children; the total incidence of the separation anxiety, loss of control and pain reaction in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group (p<0.05), as shown in Table 3.
| Group | Observation group (n=41) | Control group (n=41) | χ2 | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Separation anxiety | 1 (2.43) | 4 (9.75) | - | - |
| Loss of control | 2 (4.86) | 3 (7.31) | - | - |
| Pain response | 1 (2.43) | 3 (7.31) | - | - |
| Total incidence | 4 (9.75) | 10 (24.39) | 5.124 | 0.008 |
Table 3: Comparison of Mental States between the Two Groups of Children [N (%)]
Comparison of health behaviors between the two groups after nursing; the nutrition score, rest score and activity score of the children in the observation group after nursing were significantly higher than those in the control group and the differences were statistically significant (p<0.05), as shown in Table 4.
| Group | Observation group (n=41) | Control group (n=41) | χ2 | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutritional score | 12.45±0.29 | 8.56±0.56 | 6.201 | 0.005 |
| Rest score | 11.85±1.04 | 8.20±0.86 | 5.214 | 0.006 |
| Activity score | 12.03±0.86 | 8.45±0.37 | 5.124 | 0.001 |
Table 4: Comparison of Health Behaviors between the Two Groups after Nursing (x̄±s, POINTS)
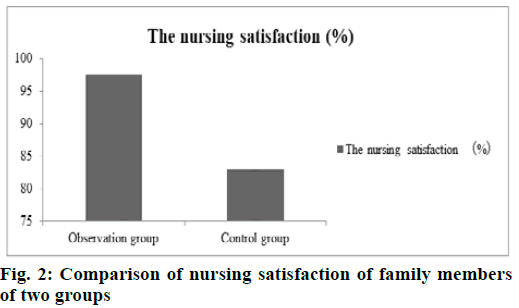
Comparison of nursing satisfaction of children’s families between two groups; the satisfaction of children with nursing in the observation group was 97.57 %, while that in the control group was 82.92 %. The satisfaction of children’s families in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group and the differences were statistically significant (p<0.05), as shown in fig. 2.
Pediatrics, as a special department, requires for a high quality nursing. With the rapid development of medical and health undertakings and the significant improvement of material level, people pay more attention to health and higher requirements are put forward for nursing quality[7]. In a society ruled by law, people will use legal weapons to protect their rights and interests[8]. Therefore, as for nursing in pediatrics, nursing staff should handle each nursing step well, pay attention to clinical nursing management according to nursing objectives and avoid undesirable phenomena in their work[9]. MBO is a new management concept and its core concept is to nurse patients on the basis of establishing post nursing goals and to take certain rewards and punishments according to nursing outcomes. In clinical nursing, nursing staff should be trained first to provide patients with better nursing services, improve patients nursing satisfaction and reduce the occurrence of adverse events[10].
Due to the young age, undeveloped mind as well as the causes of diseases, children are more prone to crying, which seriously affects the treatment of diseases and the emotions of children will also affect the family members to a certain extent. Therefore, the emotions of patients and their families should be taken into account during the nursing, which significantly increases the difficulty of nursing. According to the research of Gill FJ et al.[11], the nursing efficiency of psychological nursing strategy in pediatric inpatients is significantly higher than that of routine nursing intervention. Christian BJ et al.[12] found that the nursing quality of MBO based psychological nursing is significantly higher than that of conventional nursing methods. In the above research, the nursing effective rate of children in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group, suggesting that the MBO based psychological nursing has a significant application effect in pediatric inpatients. In the above study, the total incidence of separation anxiety, loss of control and pain reaction in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group. Thus, MBO based psychological nursing can significantly improve patients psychological state and stabilize their emotions, which is consistent with the research results of Frankenberger WD et al.[13]. In the research of Wang Y et al.[10] scholars, MBO has a remarkable clinical application value, which can promote the physical rehabilitation of patients. In the study, the nutrition score, rest score and activity score of the children in the observation group after nursing were significantly higher than those in the control group. Hence, MBO based psychological nursing can improve patients compliance with treatment and curative effect, which is consistent with the research results of the above scholars. Quinn BL et al.[14] found that this nursing method can relieve the worries of patients families about hospital treatment and improve the doctor patient relationship when studying psychological nursing under the goal theory. In the above study, the satisfaction of family members of patients in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group, suggesting that MBO based psychological nursing can alleviate the doctor patient relationship and reduce the incidence of doctor patient disputes. This may be related to not only nursing patients, but also patient communication with patient’s families. This is in line with the research results of the above scholars and Tubbs-Cooley HL et al.[15].
To sum up, MBO based psychological nursing can improve the health behavior of pediatric inpatients and the nursing satisfaction of patient’s families, which has high clinical value. Thus, it is worthy of further clinical application.
Acknowledgements:
This work was supported by the Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Xi Ding and Qing Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Conflicts of Interest:
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
References
- Silva LF, Paiva ED. Nursing interventions in palliative care in pediatric oncology: an integrative review. Rev Bras Enferm 2019;72(2):531-40.
- Stotts JR, Lyndon A, Chan GK, Bekmezian A, Rehm RS. Nursing surveillance for deterioration in pediatric patients: An integrative review. J Pediatr Nurs 2020;50:59-74.
- Goes FG, Silva AC, Santos AS, Pereira-Avila FM, Silva LJ, Silva LF. Challenges faced by pediatric nursing workers in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic. Rev Lat Am Enferm 2020;28.
- Uhm JY, Ko Y, Kim S. Implementation of an SBAR communication program based on experiential learning theory in a pediatric nursing practicum: A quasi-experimental study. Nurse Educ Today 2019;80:78-84.
- Silva-Rodrigues FM, Hinds PS, Nascimento LC. The Theory of unpleasant symptoms in pediatric oncology nursing: A conceptual and empirical fit. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs 2019;36(6):436-47.
- Li W. Application effect of management by objectives in clinical nursing management. Chin Med Clin 2019;9(1):33-40.
- Sun DH, Li L, Wang SS. Study on the effect of optimizing the practice environment of specialist nurses based on post target management. J Nurs 2020;7(9):4517-22.
- Shao FZ, Jiang YC, Zhao XY. Effect of psychological nursing intervention on psychological status of children with nephrotic syndrome. Int J Psychiatry 2019;8(3):970-2.
- Smith W. Concept analysis of family-centered care of hospitalized pediatric patients. J Pediatr Nurs 2018;42:57-64.
- Wang Y, Guo XB, Lu ZH. Standardized management of nursing adverse events based on the concept of management by objectives. J Nurs 2020;5(6):120-3.
- Gill FJ. Pediatric critical care nursing education and certification really matters. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2018;19(8):779-80.
- Christian BJ. Translational research-focusing on quality of pediatric nursing care and reducing safety risks for children and families. J Pediatr Nurs 2019;46:118-20.
- Frankenberger WD, Pasmann A, Noll J, Abbadessa MK, Sandhu R, Brodecki D, et al.Nursing research priorities in the pediatric emergency care applied research network (PECARN): reaching consensus through the Delphi method. J Emerg Nurs 2019;45(6):614-21.
- Quinn BL, Fantasia HC. Forming focus groups for pediatric pain research in nursing: a review of methods. Pain Manag Nurs 2018;19(3):303-12.
- Tubbs-Cooley HL, Mara CA, Carle AC, Mark BA, Pickler RH. Association of nurse workload with missed nursing care in the neonatal intensive care unit. JAMA Pediatr 2019;173(1):44-51.